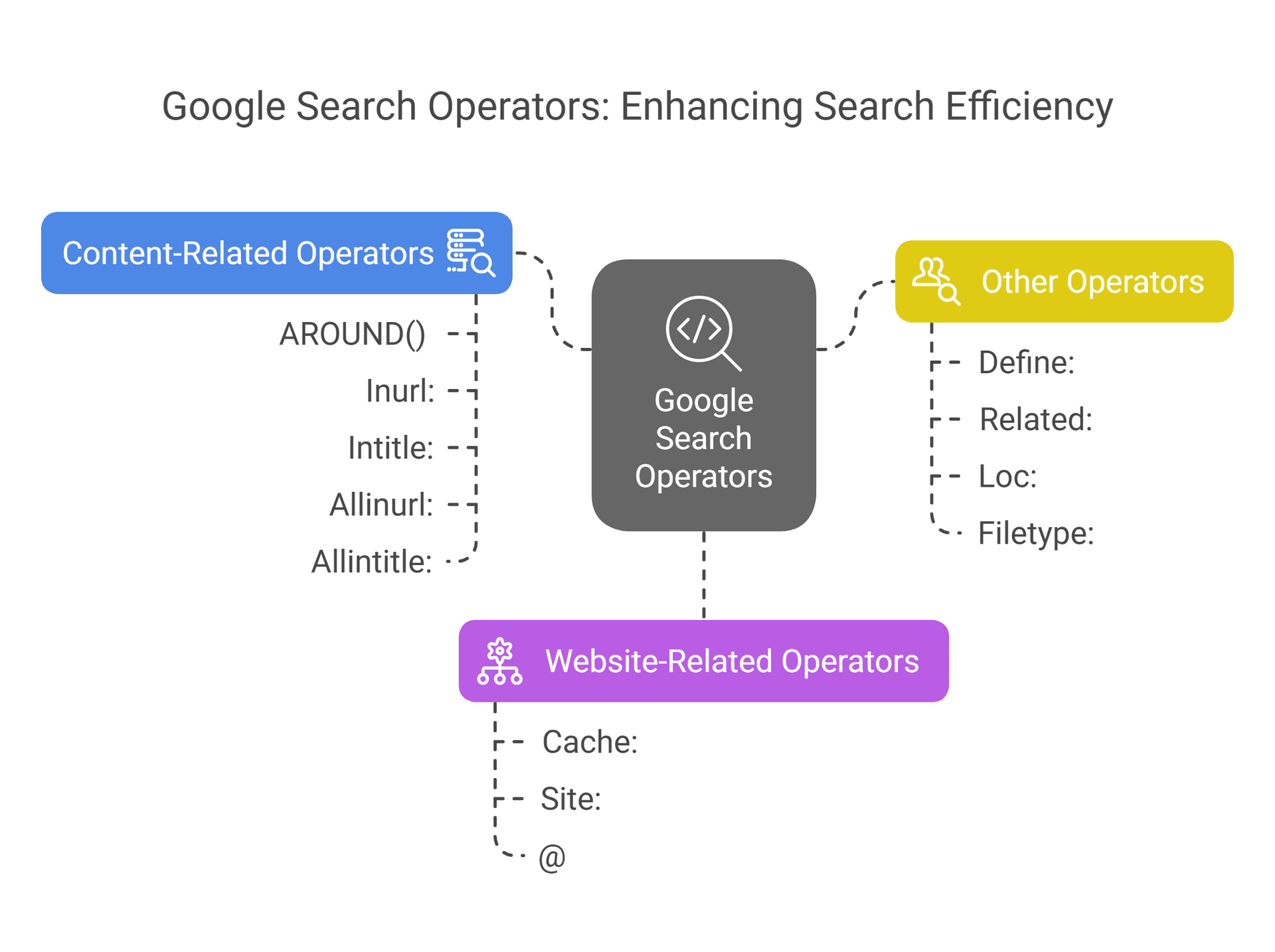
Why Use Google Search Commands?
In today's digital age, where information flows ceaselessly, quickly finding precise data is paramount. Google Search operators are your secret weapon in this quest for knowledge. They transform your basic search into a laser-focused tool, cutting through the noise and delivering precisely what you need.
Think of Google search operators as cheat codes for Google searches. Instead of typing random keywords and hoping for the best, these commands allow you to communicate with Google in a language it understands, resulting in super-targeted, relevant results.
How Google Search Operators Help:
- Narrow your search: Retrieve results from a specific website or find pages with certain words.
- Exclude unwanted results: Tell Google what you don't want to see.
- Discover exact phrases: Pinpoint specific information with precision.