Google indexing is the foundation of online visibility. Without it, your website or web pages won't appear in search results, making your content invisible to most internet users. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the technical aspects of Google Index Checking, providing you with the knowledge and tools to ensure your website's optimal performance in search engine rankings.
What is Google Indexing?
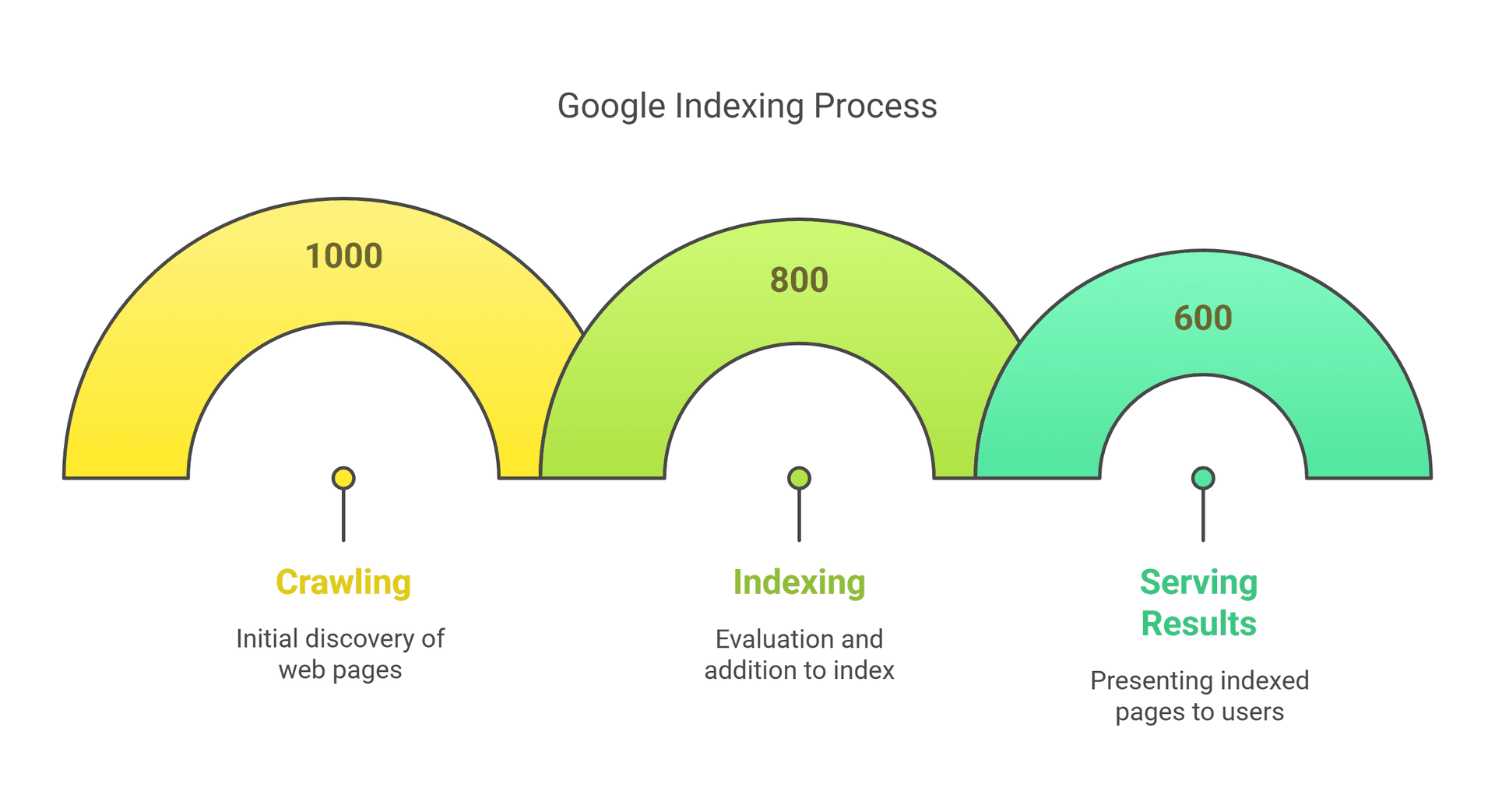
Google indexing is the process by which Google's "spiders" (automated programs called crawlers) discover, analyze, and store your web pages in a massive database called the Google Index. Google uses this index to serve relevant results when users perform searches.
Think of it like a library: Google is the librarian, the index is the card catalog, and your web pages are the books. When someone searches for information, Google consults its index (the card catalog) to find the most relevant and authoritative "books" (web pages) to present to the user.
Only indexed pages can appear in Google's search results. If a page isn't indexed, it's as if it doesn't exist in the eyes of Google, regardless of how informative or well-designed it might be.
Why is Google Indexing Important?
Google indexing is critical for several reasons: